Week 9 Tutorial
Recorded videos (Thanks Will!)
Insertion Sort
Insertion Sort is a sorting algorithm that takes one element at a time and compares it with the elements prior to it.
Example:
Let’s consider the array [33, 12, 45, 9, 24]
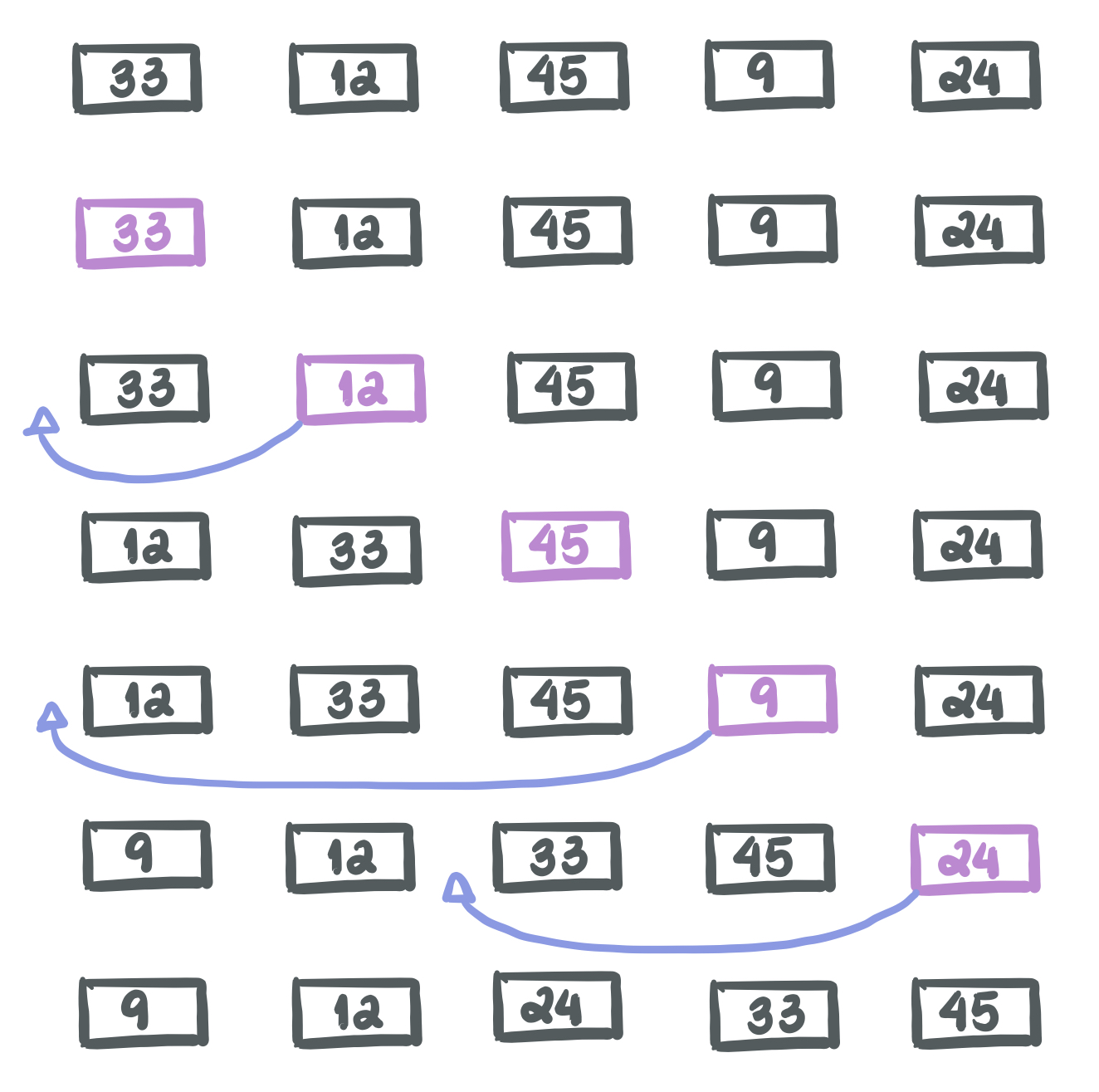
How can we implement it?
Our goal is to sort an array of n elements: [a0, a1, a2, …, an-1]
We are going to grab each element one by one, in order, and compare it with all the previous elements, which will be already sorted.
Pseudocode
- Loop through the n elements of the array
- Get the ith element
- Move the the elements of the subarray [a0, a1, …, ai-1] that are greater than the ith element.
Starter Code
# include <math.h>
# include <stdio.h>
void insertionSort(int arr[], int n) {
// Use the pseudocode to complete this part
}
int main(){
int array[] = {33, 12, 45, 9, 24};
insertionSort(array, 5);
// Print to double check
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
printf("%d ", array[i])
}
}
Discussion
Sort the following arrays by traversing through your code. How many steps does it take to complete the sort?
[33, 12, 45, 9, 24][1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6][2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 1][6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
Which one took longer?
Selection Sort
Selection Sort is a sorting algorithm that in every iteration, finds the minimum element that has not being sorted and moves it at the beginning of the array.
Example:
Let’s consider, again, the array [33, 12, 45, 9, 24]
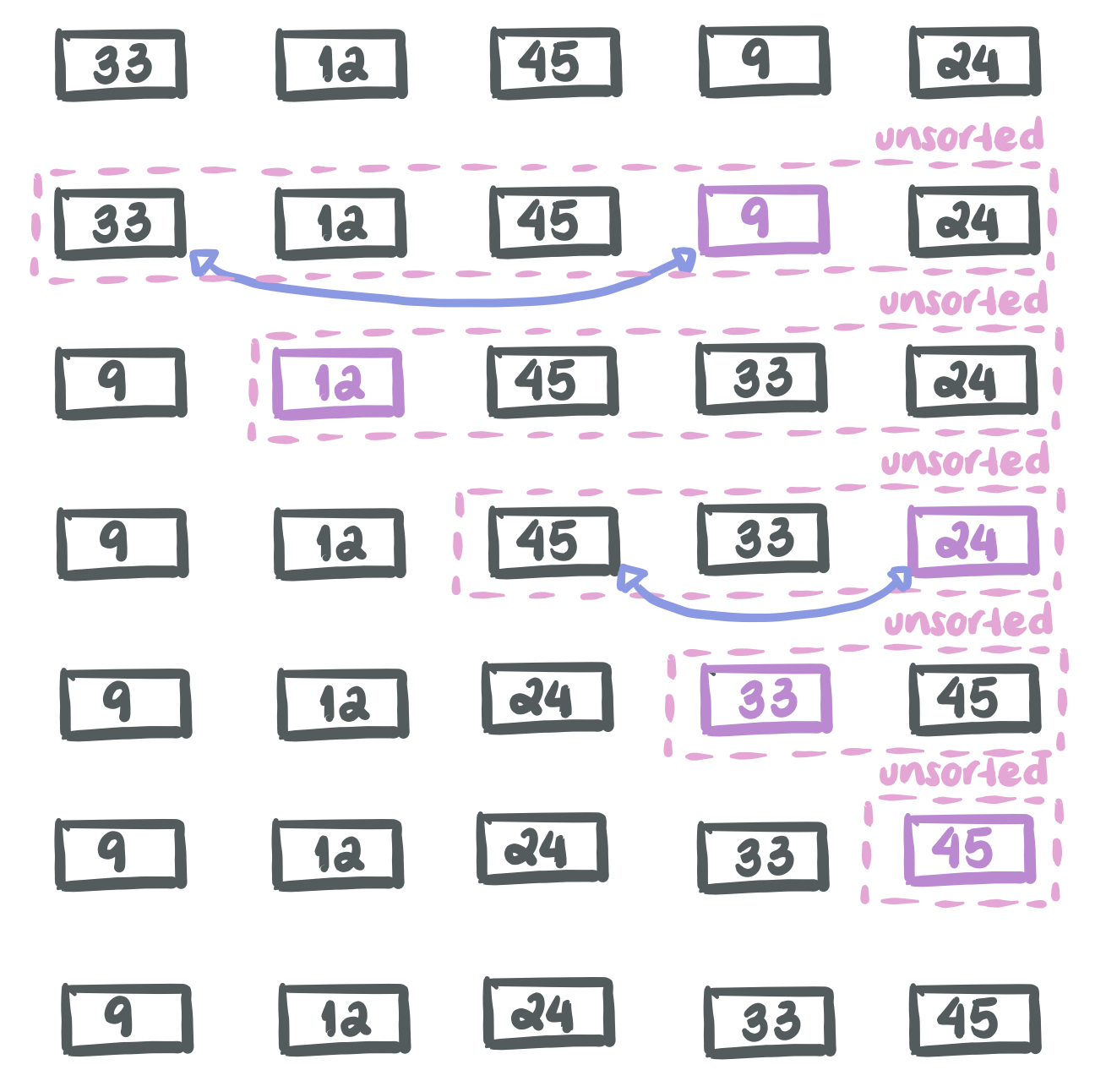
How can we implement it?
Our goal is to sort an array of n elements: [a0, a1, a2, …, an-1]
We are going to find the smallest element of the array and move it at the front to create a sorted array. We will pretty much divide the array into a sorted subarray (the beginning) and the unsorted array (the reminder - elements that haven’t been sorted yet). We will swap the found minimum element with the first element of the unsorted portion of the array.
Pseudocode
- Loop through the n elements of the array
- Find the minimum element in the unsorted portion of the array
- Swap the found minimum element with the first element of the unsorted portion.
Starter Code
# include <stdio.h>
void selectionSort(int arr[], int n) {
// Use the pseudocode to complete this part
}
int main(){
int array[] = {33, 12, 45, 9, 24};
selectionSort(array, 5);
// Print to double check
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
printf("%d ", array[i])
}
}
Discussion
Sort the following arrays by traversing through your code. How many steps does it take to complete the sort?
[33, 12, 45, 9, 24][1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6][2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 1][6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
Which one took longer? Are the results similar to the Insertion Sort?